Automate workflows with Argo
Argo Workflows is an open source container-native workflow engine for orchestrating parallel jobs on Kubernetes. In other words, Argo helps you run a sequence of tasks or functions without you having to be present (it will manage the server resources for you). Argo workflows comes enabled by default with Nebari deployments.
Access control for Argo on Nebari is done through Keycloak user groups. All
users in the admin or developer groups have access to Argo.
Also see the Set up Argo Workflows documentation.
Access the Argo Server
If Argo Workflows is enabled, users can access Argo Workflows UI at:
your-nebari-domain.com/argo. Log in via Keycloak with your usual credentials.
You can also download the Argo CLI if you prefer a command line experience.
Introduction to the Argo UI
Navigate to the Argo UI at your-nebari-domain.com/argo.
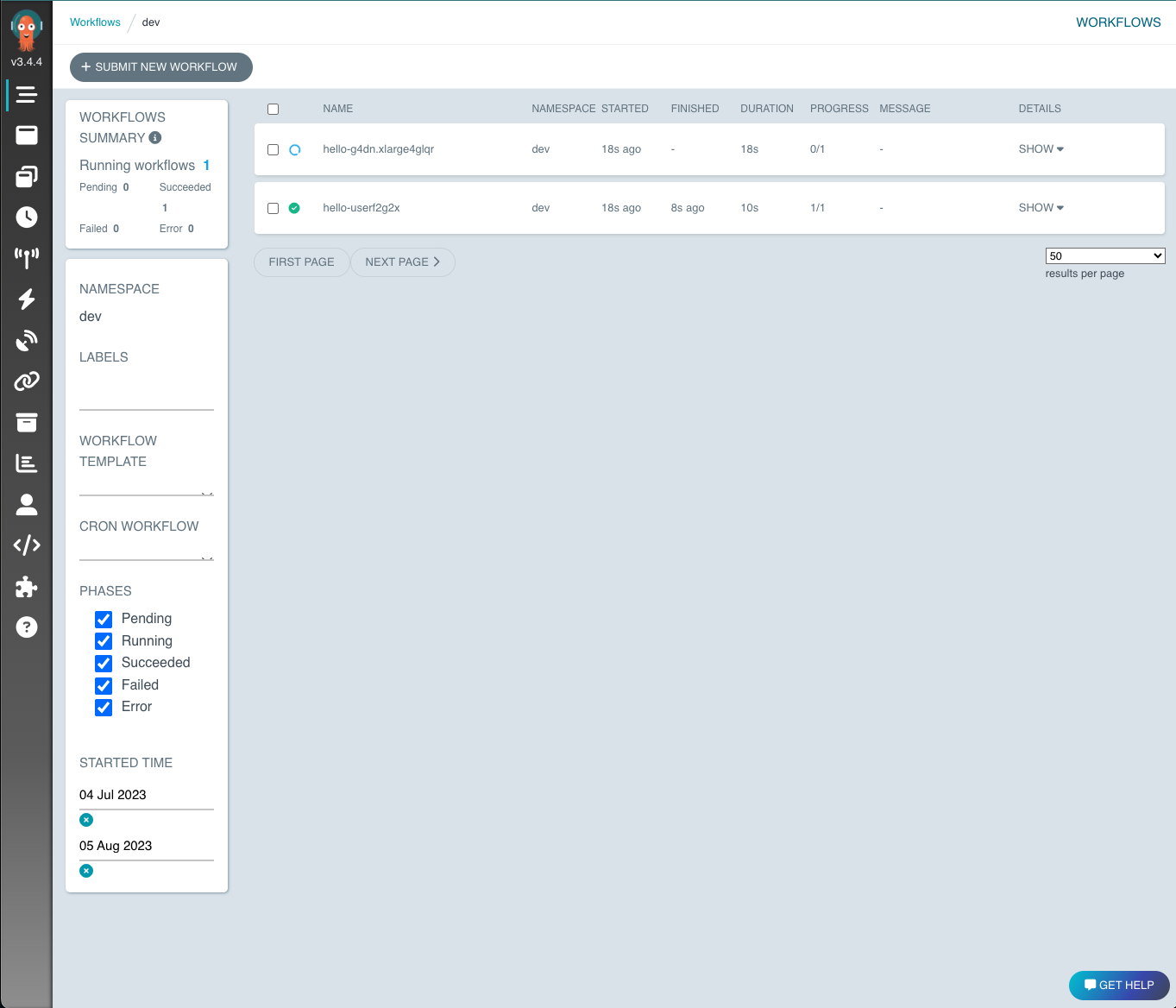
From this page, you can see all the Argo servers currently running for each workflow.
For kubernetes deployments, it important to note that these are active pods. The two workflows shown in the UI above indicate that the workflows are complete (the green check), but that the server is still running.
We highly recommend setting the default timeout, otherwise the Argo pods will not be culled on their own!
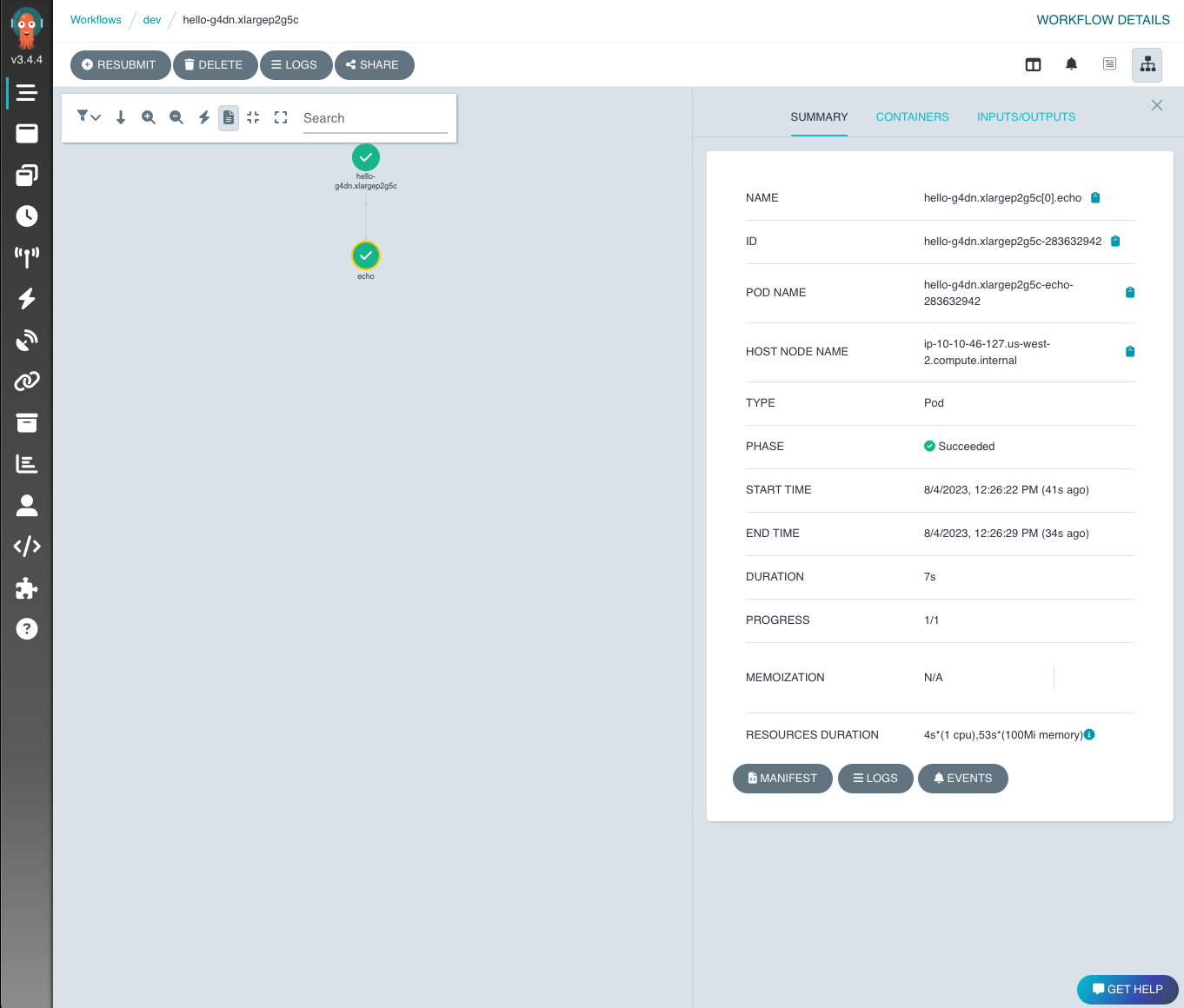
You can click on each individual workflow to see the DAG and details for each step in the workflow.
Submit a workflow
You can submit a workflow through the UI by clicking "+ SUBMIT NEW WORKFLOW" on the landing page. Argo offers a template for the workflow yaml format.
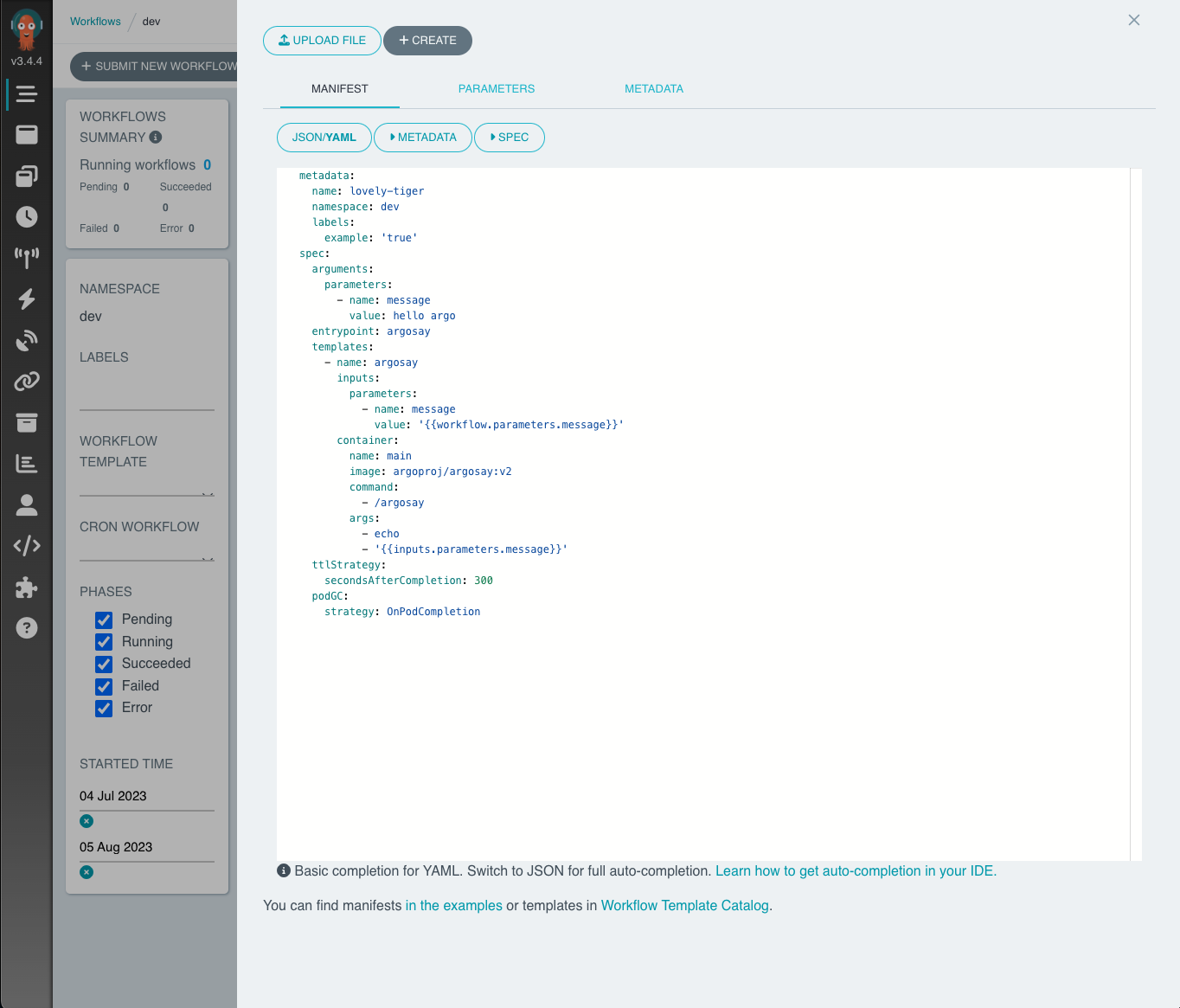
Click + CREATE when you're ready to submit. The yaml format is not the only
option for generating workflows. Argo also allows you to create workflows via
python. More information on how to generate these specifications will follow.
Submit a workflow via Argo CLI
You can also submit or manage workflows via the Argo CLI. The Argo CLI can be downloaded from the Argo Releases page.
You can submit a workflow through the CLI using argo submit my-workflow.yaml.
The argo list command will list all the running workflows.
If you've just submitted a workflow and you want to check on it, you can run
argo get @latest to get the latest submitted workflow.
You can also access the logs for a workflow using
argo logs -n workflow_name @latest.
For more information on Argo workflows via the UI or the CLI, you can visit the Argo docs.
Hera is a framework for building and submitting Argo workflows in Python. Learn more in the Argo Workflows walkthrough tutorial.
Access your Nebari environments and file system while on an Argo pod (BETA)
Once you move beyond the "Hello World" Argo examples, you may realize that the conda environments and the persistent storage you have on Nebari would be really useful in your temporary Argo pods. Lucky for you, we've solved that problem for you!
Nebari comes with Nebari Workflow Controller (BETA), abbreviated as NWC, which transfers the user's environment variables, home and shared directories, docker image, and available conda environments to the server where the Workflow is running. Users can then run a script that loads and saves from their home directory with a particular conda environment.
All of these things are enabled when users add the jupyterflow-override label
to their workflow as in this example using Hera:
from hera.workflows import Workflow
Workflow(
...
labels = {`jupyterflow-override`: 'true'},
)
Behind the scenes, NWC will override a portion of the workflow spec, mount directories, etc. The label can be added to the Workflow in a kubernetes manifest, via Hera, the Argo CLI, or via the Argo Server Web UI.
This feature requires that you have a Jupyter user pod running when the "jupyterflow-override" workflow is submitted. The workflow will not be created if you don't have a Jupyter user pod running.
YAML Example
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
name: jupyterflow-override-example
namespace: dev # replace with your deployment namespace if needed
labels:
jupyterflow-override: 'true'
spec:
entrypoint: print-hello-world
templates:
- name: print-hello-world
container:
name: main
image: any-image:any-tag # will be overridden with the jupyter user pod image
command:
- sh
- "-c"
args:
- "conda run -n nebari-git-dask python -c \"print('hello world')\" >> output_file_in_home_dir.txt"
The command starting with "conda run" runs the python print statement with the nebari-git-dask conda environment and writes stdout to the user's home directory, but could just as easily run a script in the user's home directory. The example above is for a Workflow, but the same process will work with CronWorkflows as well. In that case, the Jupyter user pod only needs to be running when the CronWorkflow is submitted, not each time the CronWorkflow starts a Workflow.
The jupyterflow-override feature is in beta so please leave some feedback and report any issues.
Additional Argo Workflows Resources
Refer to the Argo documentation for further details on Argo Workflows.
Next Steps
Now that you have had an introduction, check out the more detailed tutorial on Argo for some practical examples!